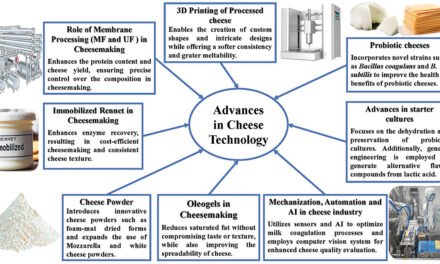
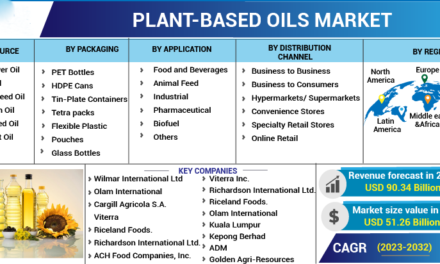
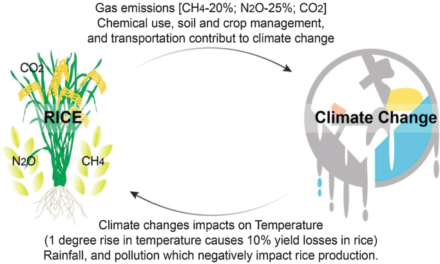
Small-scale farmers often face financial constraints that make acquiring advanced machinery challenging. However, several strategies and programs enable them to access modern equipment affordably, improving efficiency and productivity. Here’s how small-scale farmers can gain access to advanced machinery:
1. Equipment Leasing and Rental Programs
- What It Is:
- Farmers can lease or rent machinery for a specific period, eliminating the need for upfront investment.
- How It Helps:
- Reduces the financial burden as farmers pay only for the usage period.
- Enables access to advanced equipment during critical seasons, such as planting or harvesting.
- Examples:
- Community-based rental centers or private leasing companies providing tractors, plows, or harvesters.
- Mobile applications like Trringo (India) or Hello Tractor (Africa) connect farmers with machinery owners for on-demand rentals.
2. Cooperative Ownership
- What It Is:
- Farmers pool resources to jointly purchase and share machinery.
- How It Helps:
- Lowers individual costs while providing access to advanced tools.
- Fosters collaboration and resource optimization among small-scale farmers.
- Examples:
- Cooperatives purchasing threshers or combine harvesters for shared use during harvest season.
3. Government Subsidy and Grant Programs
- What It Is:
- Governments often provide subsidies or grants to farmers for purchasing agricultural machinery.
- How It Helps:
- Makes advanced machinery affordable by covering a portion of the purchase cost.
- Encourages adoption of modern farming techniques.
- Examples:
- Subsidies for Farm Mechanization: Many countries offer discounts or direct financial support for purchasing tractors, seed drills, or irrigation pumps.
- Grants for Sustainable Agriculture: Funding for solar-powered pumps or electric tractors to promote eco-friendly practices.
4. Second-Hand Machinery Markets
- What It Is:
- Farmers can purchase pre-owned machinery at significantly reduced prices.
- How It Helps:
- Provides cost-effective access to functional equipment.
- Ideal for tools that retain value over time, such as plows, tillers, or seed drills.
- Examples:
- Online marketplaces or local auctions specializing in used agricultural equipment.
5. Custom Hiring Centers (CHCs)
- What It Is:
- Government or private entities establish centers that provide machinery and equipment on a pay-per-use basis.
- How It Helps:
- Farmers access high-cost machinery without owning it.
- Promotes equitable access to technology in rural areas.
- Examples:
- India’s CHC Scheme provides affordable access to tractors, harvesters, and other machinery for small-scale farmers.
6. Farmer-Entrepreneur Partnerships
- What It Is:
- Entrepreneurs or machinery owners offer services to farmers for a fee, using their equipment on multiple farms.
- How It Helps:
- Small farmers pay only for the service, avoiding capital investment.
- Entrepreneurs maintain and transport machinery, reducing operational hassle for farmers.
- Examples:
- A local entrepreneur operates a combine harvester for a group of farmers during the harvest season.
7. Crowdfunding and Community Support
- What It Is:
- Farmers raise funds through community-based crowdfunding platforms or agricultural cooperatives.
- How It Helps:
- Provides financial assistance for purchasing machinery.
- Strengthens local networks and community support for mechanization.
- Examples:
- Online crowdfunding platforms focused on agriculture, such as Kickstarter or GoFundMe.
8. Agricultural Machinery Banks
- What It Is:
- Machinery banks are community facilities that store equipment for farmers to borrow at a nominal fee.
- How It Helps:
- Offers low-cost access to a variety of tools and machines.
- Reduces redundancy and promotes efficient machinery usage.
- Examples:
- FAO’s Mechanization Program supports establishing machinery banks in developing countries.
9. Partnerships with NGOs and Development Programs
- What It Is:
- Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and international agencies provide funding or direct access to machinery.
- How It Helps:
- Introduces modern tools to marginalized farming communities.
- Encourages adoption of sustainable and efficient farming practices.
- Examples:
- Programs by the World Bank, FAO, or local NGOs to distribute irrigation systems, threshers, or solar-powered equipment.
10. Financial Assistance and Loan Programs
- What It Is:
- Farmers can secure loans tailored for agricultural equipment purchases.
- How It Helps:
- Spreads the cost of machinery over manageable installments.
- Low-interest loans or flexible repayment schedules make high-cost tools accessible.
- Examples:
- Kisan Credit Card (India): Offers credit for agricultural machinery at subsidized interest rates.
- Agricultural Equipment Financing Programs by commercial banks.
11. Multi-Functional Machinery
- What It Is:
- Tools designed for multiple purposes, such as plowing, planting, and spraying.
- How It Helps:
- Reduces the need to buy separate machines for each task.
- Saves costs and storage space.
- Examples:
- A multi-crop planter that works for maize, wheat, and rice.
12. Training and Capacity Building
- What It Is:
- Training programs help farmers operate advanced machinery efficiently and safely.
- How It Helps:
- Reduces the risk of equipment misuse or damage.
- Increases productivity and ensures long-term benefits.
- Examples:
- Government or NGO-organized workshops on using drones, precision sprayers, or smart irrigation systems.
13. Flexible Payment Plans from Manufacturers
- What It Is:
- Equipment manufacturers offer installment-based payment plans or lease-to-own models.
- How It Helps:
- Farmers can gradually pay off the cost while using the machinery.
- Reduces the financial barrier to acquiring modern equipment.
- Examples:
- Lease-to-own tractors from companies like John Deere or Mahindra.
14. Adoption of Electric-Powered Tools
- What It Is:
- Affordable electric-powered tools like sprayers, tillers, or pumps reduce costs compared to diesel-powered options.
- How It Helps:
- Low operational costs and minimal maintenance requirements.
- Environmentally friendly and suitable for small-scale farms.
- Examples:
- Battery-powered weeders or sprayers for small vegetable farms.
15. Integration of Digital Platforms
- What It Is:
- Mobile apps and online platforms connect farmers with equipment rental, leasing, or purchase options.
- How It Helps:
- Provides transparency in pricing and availability.
- Simplifies access to machinery through digital tools.
- Examples:
- Platforms like Tractor Junction (India) or Farmers Friend (Africa) offer machinery rentals and sales.
Conclusion
Small-scale farmers can access advanced machinery affordably through innovative strategies like leasing, cooperative ownership, government subsidies, and partnerships with NGOs. Leveraging rental services, flexible financing, and shared ownership models allows farmers to benefit from modern tools without heavy financial burdens. These approaches empower farmers to improve productivity, reduce labor costs, and enhance sustainability, ensuring long-term success in agriculture.
Hashtags
#FarmToTable #OrganicFarming #CommunitySupportedAgriculture #FarmersMarket #LocalFoodMovement #FarmLife #FarmersOfInstagram #FarmFresh #FarmersSupportingFarmers #FarmersFirst #FarmersPride #FarmersUnited #FarmersSuccess #FarmersGrowth #FarmersFuture #FarmersInspiration #FarmersEmpowerment #FarmersInnovate #FarmersSustainability #FarmersProgress