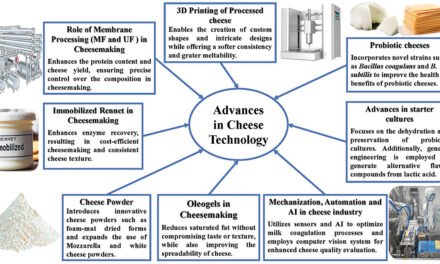
Developing lactose-free dairy products presents several challenges that manufacturers must navigate to ensure product quality, functionality, and consumer acceptance. These challenges span technological, sensory, economic, and marketing dimensions:
1. Maintaining Taste and Texture
- Flavor Alterations: Removing lactose or breaking it down into glucose and galactose during processing can affect the sweetness and flavor profile of dairy products.
- Texture Issues: Lactose contributes to the mouthfeel and structure of products like ice cream, cheese, and yogurt, so its removal can result in undesirable changes.
2. Processing Complexity
- Enzymatic Hydrolysis: Using lactase enzymes to break down lactose requires precise control to avoid over-processing, which can lead to off-flavors or textural inconsistencies.
- Cross-Contamination: Preventing traces of lactose in “lactose-free” products requires rigorous cleaning and monitoring of equipment and production lines.
- Adaptation of Traditional Recipes: Many traditional dairy processes rely on lactose’s properties, requiring significant reformulation.
3. Cost Implications
- Enzyme Costs: Lactase enzymes used for lactose breakdown can be expensive, increasing production costs.
- Specialized Equipment: Additional filtration systems (e.g., ultrafiltration) or separate processing lines for lactose-free products add to operational expenses.
- Raw Material Selection: Sourcing lactose-free or low-lactose milk ingredients may involve premium pricing.
4. Shelf-Life Management
- Microbial Stability: Breaking down lactose into simpler sugars can increase the risk of microbial spoilage, potentially shortening shelf life.
- Sugar Balance: Higher glucose and galactose levels from lactose hydrolysis may impact the preservation characteristics of the product.
5. Regulatory and Labeling Compliance
- Strict Standards: Products labeled as “lactose-free” must meet stringent regulatory requirements, often necessitating rigorous testing.
- Regional Variations: Different countries have varying definitions and thresholds for lactose-free or low-lactose products.
6. Consumer Acceptance
- Perception of Taste: Consumers accustomed to traditional dairy products may detect and dislike subtle changes in flavor or sweetness.
- Preference for “Natural” Products: Some consumers may avoid lactose-free dairy due to concerns over the use of enzymes or other processing techniques.
7. Product-Specific Challenges
- Milk: Ensuring the same creamy mouthfeel in lactose-free milk can be difficult without lactose.
- Cheese: Lactose plays a role in cheese maturation, and its absence can affect flavor complexity and texture.
- Yogurt: Probiotic cultures in yogurt often rely on lactose for fermentation, making it challenging to maintain the same probiotic activity in lactose-free versions.
- Ice Cream: Achieving the same creaminess and freezing properties in lactose-free ice cream requires reformulating with alternative sugars or stabilizers.
8. Limited Awareness and Market Dynamics
- Educating Consumers: Many consumers confuse lactose-free products with dairy-free alternatives, necessitating clear marketing and education.
- Demand Fluctuation: In markets where lactose intolerance is less prevalent, the demand for lactose-free products may not justify the investment.
9. Innovation and Ingredient Sourcing
- Alternative Sweeteners: Balancing sweetness without introducing off-flavors or artificial sweeteners is a challenge for many manufacturers.
- Functional Ingredients: Developing lactose-free versions of dairy products often requires experimenting with new stabilizers or emulsifiers, which may affect overall formulation.
10. Competition with Plant-Based Alternatives
- Consumer Shift: The growing popularity of plant-based dairy alternatives, perceived as healthier or more sustainable, creates competition for lactose-free dairy products.
- Innovation Pressure: To compete, lactose-free dairy must match or exceed the sensory and nutritional profile of plant-based options.
Strategies to Overcome Challenges
- Advanced Technologies: Techniques like ultrafiltration, chromatography, or fermentation are being employed to remove or neutralize lactose effectively.
- Product Reformulation: Using natural stabilizers and flavor enhancers to compensate for changes in sweetness and texture.
- Consumer-Centric Approach: Conducting sensory tests and educating consumers about the benefits and taste of lactose-free dairy products.
- Collaborative R&D: Partnering with ingredient suppliers and food technologists to develop innovative solutions for lactose-free production.
By addressing these challenges through innovation and strategic planning, manufacturers can successfully tap into the growing demand for lactose-free dairy products.