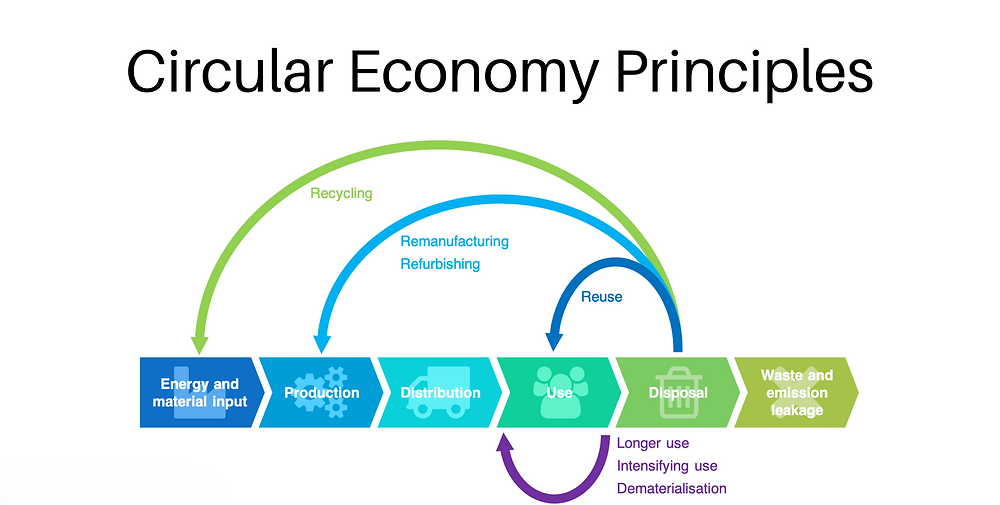
Circular economy principles are set to play a transformative role in the future of agricultural manufacturing by promoting resource efficiency, waste reduction, and sustainable practices. Here are the key aspects of their influence:
1. Waste Minimization and Resource Recovery
- Utilization of By-Products: Agricultural manufacturers will increasingly repurpose by-products, such as fruit peels, husks, and crop residues, into valuable inputs like biofuels, animal feed, or natural fertilizers.
- Food Waste Reduction: Unsold or surplus products may be redirected for secondary use in processed foods, composting, or energy generation through anaerobic digestion.
2. Sustainable Packaging Solutions
- Biodegradable Packaging: Manufacturers will adopt eco-friendly packaging made from agricultural waste, such as cornstarch, sugarcane, or cellulose, reducing reliance on plastics.
- Closed-Loop Packaging: Systems encouraging the return and recycling of packaging materials, such as glass bottles or reusable containers, will become more widespread.
3. Efficient Use of Resources
- Water and Energy Efficiency: Circular economy principles emphasize reducing water and energy consumption in agricultural manufacturing through technologies like precision irrigation and renewable energy integration.
- Nutrient Recycling: Nutrients extracted during processing can be reintroduced into farming systems, supporting soil fertility and reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
4. Lifecycle Management of Products
- Cradle-to-Cradle Design: Products will be designed with the entire lifecycle in mind, ensuring that materials can be reused, recycled, or composted at the end of their use.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): Manufacturers may take responsibility for the disposal or recycling of their products and packaging, encouraging sustainable practices throughout the supply chain.
5. Integration of Renewable Inputs
- Bio-Based Materials: The use of renewable raw materials from plants or agricultural waste will replace finite resources in the manufacturing process.
- Circular Supply Chains: Partnerships with farmers and suppliers will focus on regenerating ecosystems and ensuring the continuous flow of sustainable raw materials.
6. Digital and Technological Advancements
- Data-Driven Optimization: Technologies like IoT, AI, and blockchain will help track resource usage and minimize waste throughout the production cycle.
- Smart Waste Management: Advanced sorting, recycling, and composting systems will be implemented to manage agricultural and manufacturing waste efficiently.
7. Economic and Social Benefits
- Cost Savings: Circular practices can lower production costs by reducing waste and maximizing the value extracted from raw materials.
- Job Creation: New roles in recycling, remanufacturing, and sustainable innovation will emerge as industries transition to circular models.
8. Collaboration Across the Value Chain
- Industry Partnerships: Collaboration among farmers, manufacturers, retailers, and consumers will be crucial to establishing closed-loop systems and shared sustainability goals.
- Policy and Incentives: Governments and organizations may provide incentives or mandates to encourage circular economy adoption within agricultural manufacturing.
By integrating circular economy principles, agricultural manufacturing can achieve greater sustainability, resilience, and efficiency, contributing to a more balanced and regenerative food system.