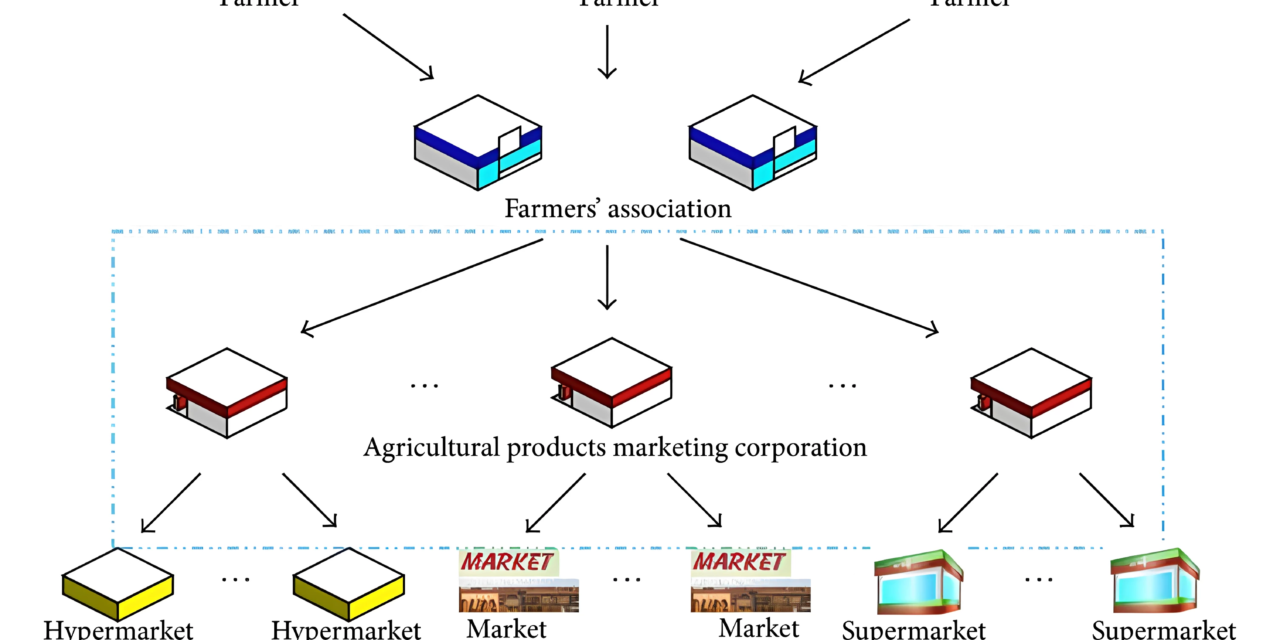
Recent global supply chain disruptions have significantly impacted the manufacturing of agricultural products, affecting everything from raw material sourcing to final product distribution. Key developments include:
The agricultural sector is facing substantial transportation issues, leading to increased costs and delays. Rising freight prices and labor shortages have made moving raw materials and fresh produce more expensive and slower. These challenges are expected to result in higher food prices for consumers.
There is a growing emphasis on sustainable and traceable agricultural supply chains. Regulations like the European Union’s Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) require companies to ensure their products have not contributed to deforestation. This has led to increased demand for technologies that enhance supply chain transparency and sustainability.
Climate change is exacerbating supply chain vulnerabilities, affecting crop yields and food security. Extreme weather events have led to significant losses in agricultural production, contributing to higher food prices and supply shortages. Addressing these challenges requires building climate-resilient food supply chains through international cooperation and investment in adaptive technologies.
Geopolitical tensions and conflicts, such as the Russia-Ukraine war, have disrupted global food supply chains. These disruptions have led to shortages and price increases for various agricultural products, highlighting the interconnectedness of global food systems. The agricultural manufacturing sector is navigating a complex landscape of transportation challenges, regulatory pressures, climate change impacts, and geopolitical factors. Addressing these issues requires a multifaceted approach, including investment in sustainable practices, technological innovation, and international collaboration to enhance supply chain resilience.