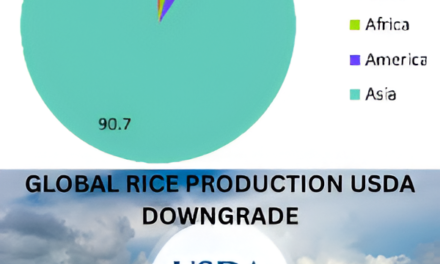
The rise of e-commerce has revolutionized the distribution of packaged goods in India, transforming how products are delivered, consumed, and marketed across urban and rural markets. The rapid digitalization of India, coupled with widespread smartphone penetration and affordable internet access, has made online platforms the preferred shopping destination for FMCG (Fast-Moving Consumer Goods) such as food, beverages, personal care, and household essentials. This shift has not only accelerated convenience but also broadened market access for both consumers and businesses.
Major e-commerce players like Amazon, Flipkart, BigBasket, JioMart, and grocery-focused platforms have streamlined the supply chain, offering a seamless shopping experience with features such as quick delivery, cash-on-delivery options, and easy returns. Startups and Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) brands have emerged as significant players, leveraging e-commerce to connect directly with consumers and bypass traditional retail intermediaries. This has enabled smaller brands to scale quickly, introducing innovative and niche products such as health foods, organic snacks, eco-friendly packaging, and gourmet packaged goods.
The pandemic further accelerated the adoption of online channels, with consumers prioritizing hygiene, safety, and convenience. Categories like ready-to-eat meals, packaged beverages, snacks, and essential household products saw exponential growth in demand. E-commerce platforms responded with innovations like hyperlocal delivery, enabling quicker fulfillment of orders through tie-ups with local stores and warehouses.
Rural markets have also benefited significantly from this revolution. The expansion of last-mile connectivity and improved logistics infrastructure has enabled e-commerce to penetrate Tier 2, Tier 3, and rural areas, where access to diverse packaged goods was previously limited. Platforms like JioMart and Flipkart have made branded products accessible in smaller towns and villages, fulfilling demand for affordable and value-for-money offerings through cost-effective packaging, such as low-unit price (LUP) packs.
Moreover, technology is playing a transformative role. The use of AI and machine learning for demand forecasting, warehouse optimization, and personalized recommendations has enhanced operational efficiency and consumer satisfaction. Brands are also utilizing data analytics to gain deeper insights into purchasing behavior, enabling them to tailor products and promotions to specific regional preferences.
E-commerce has also supported the shift towards sustainable consumption. Many platforms now highlight products with eco-friendly packaging, organic ingredients, and health-conscious options, further driving trends in clean-label and premium packaged goods. Additionally, the integration of digital payments and fintech solutions has simplified transactions, boosting online shopping adoption even in areas with limited banking infrastructure.
The e-commerce revolution has fundamentally transformed the distribution landscape of packaged goods in India, enabling companies to reach untapped markets, reduce operational costs, and enhance customer engagement. As digital infrastructure continues to improve and consumer behavior further shifts toward online purchasing, e-commerce is set to play an even more critical role in driving the growth and accessibility of packaged goods across the country.