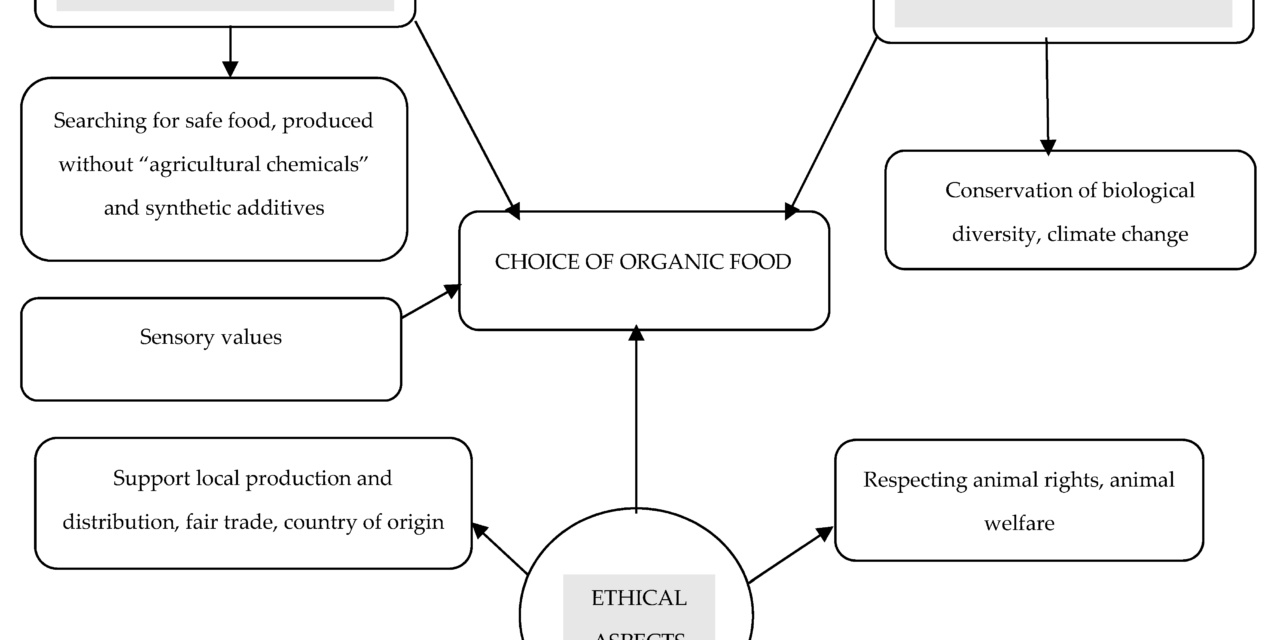
Consumer preferences for organic products significantly shape the food, beverage, and personal care industries by driving changes in production, marketing, supply chains, and product innovation. Here’s how this growing demand is influencing the industry:
1. Growth of the Organic Market
- Impact: Increasing consumer interest in health, sustainability, and ethical practices has fueled a surge in organic product demand.
- Industry Response:
- Expansion of organic product portfolios, including snacks, beverages, cosmetics, and baby food.
- Entry of mainstream brands into the organic segment to capture market share.
- Example: Large food companies like General Mills and Nestlé have acquired or launched organic product lines.
2. Shift Towards Sustainable Farming
- Impact: Organic farming practices, which avoid synthetic chemicals and GMOs, are becoming more mainstream.
- Industry Response:
- Partnerships with certified organic farmers to ensure a steady supply of raw materials.
- Investment in regenerative agriculture practices that align with organic principles.
- Example: Brands like Danone are collaborating with farmers to adopt organic and sustainable farming practices.
3. Transparency and Traceability
- Impact: Consumers expect detailed information about the sourcing and production of organic products.
- Industry Response:
- Adoption of blockchain and traceability technologies to ensure supply chain transparency.
- Certification labels like USDA Organic, EU Organic, and others are prominently displayed on the packaging.
- Example: Companies like Honest Tea and Dr. Bronner use certifications and detailed product stories to build trust.
4. Focus on Health and Wellness
- Impact: Organic products are perceived as healthier and safer, attracting health-conscious consumers.
- Industry Response:
- Reformulating products to include organic ingredients while eliminating artificial additives and preservatives.
- Introducing functional organic products, such as superfood powders, organic protein bars, and probiotic beverages.
- Example: Brands like Annie’s Homegrown offer organic versions of traditionally processed foods to cater to this demand.
5. Expansion of Organic Offerings
- Impact: Consumers seek organic options across diverse categories, from fresh produce to packaged goods.
- Industry Response:
- Growth in non-food organic sectors, such as skincare, cosmetics, and textiles.
- Development of organic convenience foods, including ready-to-eat meals and snacks.
- Example: Organic skincare brands like Burt’s Bees emphasize natural ingredients and sustainability.
6. Premium Pricing and Value Perception
- Impact: Organic products are often priced higher due to the cost of certification, farming, and processing.
- Industry Response:
- Highlighting the health, environmental, and ethical benefits of organic products to justify premium pricing.
- Offering smaller package sizes or bulk options to cater to diverse budgets.
- Example: Retailers like Costco and Whole Foods Market provide organic products in bulk to make them more accessible.
7. Influence on Retail and E-Commerce
- Impact: Organic products have spurred changes in retail strategies, including dedicated organic sections and online offerings.
- Industry Response:
- Expansion of organic product availability in mainstream grocery stores, not just niche health food markets.
- Growth of e-commerce platforms and direct-to-consumer (DTC) sales channels for organic products.
- Example: Amazon’s acquisition of Whole Foods and the development of online organic food platforms.
8. Increased Focus on Sustainability
- Impact: Organic farming’s focus on soil health, biodiversity, and water conservation aligns with sustainability goals.
- Industry Response:
- Integrating sustainable practices into the supply chain to enhance environmental benefits.
- Combining organic claims with other sustainability certifications, such as Fair Trade or Carbon Neutral.
- Example: Chocolate brands like Alter Eco combine organic and Fair Trade certifications.
9. Regulatory and Certification Challenges
- Impact: Compliance with organic standards is critical to meet consumer expectations and avoid regulatory penalties.
- Industry Response:
- Ensuring adherence to organic certification standards through rigorous audits and supplier oversight.
- Educating consumers about the meaning of organic certifications to build trust.
- Example: Companies invest in certification processes like USDA Organic and Non-GMO Project Verified.
10. Influence on Innovation
- Impact: The organic trend is driving product innovation to create new, appealing options for consumers.
- Industry Response:
- Combining organic ingredients with trending formats, such as plant-based or gluten-free products.
- Experiment with organic alternatives to conventional sweeteners, fats, and flours.
- Example: Organic kombucha, protein powders, and dairy-free ice creams are gaining popularity.
11. Challenges in Meeting Demand
- Impact: The rising demand for organic products puts pressure on supply chains.
- Industry Response:
- Increasing investment in organic farming to scale supply.
- Supporting farmers through training, financial assistance, and long-term contracts.
- Example: Organic Valley works closely with farmers to expand organic dairy production.
12. Impact on Small and Local Producers
- Impact: The organic movement supports small-scale and local producers who can meet niche consumer needs.
- Industry Response:
- Retailers promote locally sourced organic products to differentiate themselves.
- Small brands leverage direct marketing and community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs.
- Example: Farmer’s markets and CSAs offering certified organic produce directly to consumers.
ConclusiConsumer preferences for organic products are reshaping the industry by influencing production practices, product development, and marketing strategies. Companies that align with these preferences through transparency, innovation, and sustainability are well-positioned to thrive in the growing organic market.
Hashtags
#FoodAllergyAwareness #CleanEating #FoodQualityControl #AllergenTesting #SafeFoodHandling #FoodSafetyMatters #AllergyPrevention #FoodProductionStandards #CleanFoodMovement #AllergenFreeOptions #FoodSafetyCompliance #HealthyEatingChoices #AllergyFriendlyRecipes #FoodProcessingTechnology #SafeFoodHandlingPractices #AllergenAwareness #FoodSafetyRegulations #CleanLabelMovement #AllergySafeProducts #FoodIndustryInnovations