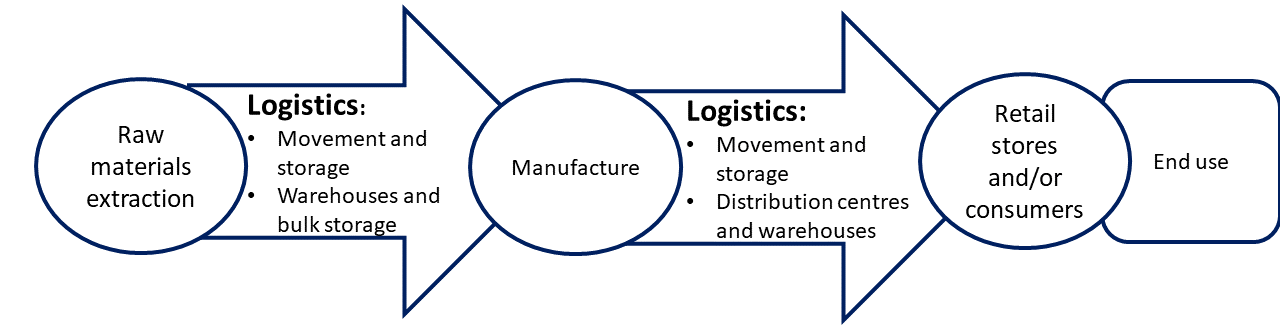
Managing supply chain logistics for perishable goods is complex and requires meticulous planning to maintain quality and minimize spoilage. Here are key strategies companies use to handle this effectively:
1. Cold Chain Management
- Temperature-Controlled Storage and Transportation:
- Use refrigerated trucks, containers, and warehouses to maintain optimal temperatures.
- Monitor and control temperature and humidity levels at all stages of the supply chain.
- Real-Time Monitoring:
- IoT-enabled sensors track conditions like temperature, humidity, and shock during transit.
- Alerts notify stakeholders of deviations to take corrective actions immediately.
2. Efficient Transportation
- Direct Routes:
- Minimize transit time by using direct or express shipping methods where possible.
- Multi-Modal Logistics:
- Combine air, sea, and land transport to optimize speed and cost while maintaining quality.
- Pre-Approved Customs Clearance:
- Use expedited customs processes to reduce delays at borders or ports.
3. Inventory and Demand Forecasting
- Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory:
- Produce and ship goods based on accurate demand forecasts to avoid overstocking or spoilage.
- Predictive Analytics:
- Leverage AI and machine learning to anticipate demand fluctuations and align production and distribution schedules.
4. Packaging Solutions
- Specialized Packaging:
- Use insulated, vacuum-sealed, or nitrogen-flushed packaging to preserve freshness and extend shelf life.
- Smart Packaging:
- Incorporate technology like freshness indicators or RFID tags to monitor product conditions.
5. Collaboration with Reliable Partners
- Third-Party Logistics (3PL):
- Partner with 3PL providers experienced in handling perishable goods and equipped with advanced cold chain facilities.
- Supplier Relationships:
- Work closely with suppliers to ensure the timely production and dispatch of high-quality goods.
6. Dynamic Route Optimization
- Use GPS and AI-based software to plan optimal delivery routes in real time, accounting for traffic, weather, and road conditions.
7. Regulatory Compliance
- Food Safety Standards:
- Ensure compliance with local and international food safety regulations (e.g., HACCP, FSMA, or EU standards).
- Documentation and Traceability:
- Maintain detailed records to trace products throughout the supply chain.
8. Risk Mitigation Plans
- Backup Systems:
- Have contingency plans for equipment failures, such as backup refrigeration units or alternative transport modes.
- Insurance:
- Protect against losses from spoilage, delays, or accidents.
9. Training and Awareness
- Train employees and partners in handling perishable goods to ensure adherence to protocols and reduce the risk of human error.
10. Sustainability Practices
- Waste Reduction:
- Repurpose or donate near-expiry goods to minimize waste.
- Energy-Efficient Technologies:
- Use renewable energy and eco-friendly cooling systems to reduce environmental impact.