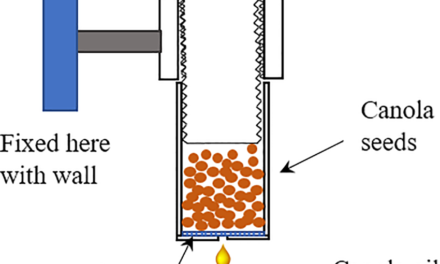
Seed drills are mechanical devices that improve planting precision by accurately placing seeds in the soil at the correct depth, spacing, and rate. This precision ensures optimal growing conditions, promotes uniform germination, and enhances crop yield and quality. Here’s how seed drills improve planting precision:
1. Uniform Seed Spacing
- How It Works:
- Seed drills use calibrated mechanisms, such as seed metering systems, to deposit seeds at consistent intervals in each row.
- Impact:
- Prevents overcrowding, which reduces competition for sunlight, water, and nutrients.
- Improves plant health and growth uniformity, making crops easier to manage and harvest.
- Example:
- In crops like corn or soybeans, precise spacing ensures each plant has adequate room to develop fully.
2. Consistent Depth Placement
- How It Works:
- Seed drills are equipped with depth control mechanisms that place seeds at the desired depth, regardless of soil texture or terrain.
- Impact:
- Ensures proper seed-soil contact, which is crucial for water absorption and germination.
- Reduces the risk of seeds being too shallow (leading to drying out) or too deep (delaying germination).
- Example:
- For wheat, planting at a depth of 1–1.5 inches ensures optimal germination and strong root establishment.
3. Accurate Seeding Rates
- How It Works:
- Seed drills allow farmers to calibrate the rate at which seeds are released, ensuring the correct number of seeds per unit area.
- Impact:
- Prevents under-seeding, which reduces yield potential, and over-seeding, which wastes resources and increases competition.
- Optimizes seed use, lowering input costs.
- Example:
- Precision in seeding rates for rice paddies helps achieve uniform plant density, reducing the risk of pest infestations.
4. Even Row Alignment
- How It Works:
- Seed drills plant seeds in straight, evenly spaced rows, ensuring uniformity across the field.
- Impact:
- Facilitates efficient irrigation, fertilization, and mechanical weeding or harvesting.
- Improves airflow between rows, reducing disease risks like fungal infections.
- Example:
- In vegetable farming, even rows make drip irrigation and mechanical harvesting more effective.
5. Reduced Seed Wastage
- How It Works:
- The precise placement mechanism minimizes the risk of seeds being broadcast unevenly, falling outside planting areas, or overlapping excessively.
- Impact:
- Maximizes the efficiency of seed use and reduces overall input costs.
- Ensures better resource allocation for large-scale farms.
- Example:
- In canola or mustard farming, small seeds are expensive, and precision planting prevents waste.
6. Adaptability to Soil Conditions
- How It Works:
- Advanced seed drills are designed to adjust to varying soil types, moisture levels, and terrain conditions.
- Impact:
- Maintains planting accuracy in challenging environments, such as rocky or compacted soils.
- Reduces the risk of uneven germination caused by inconsistent planting.
- Example:
- In no-till farming, seed drills ensure seeds are planted effectively without disturbing the soil structure.
7. Time and Labor Efficiency
- How It Works:
- Seed drills automate the planting process, reducing the need for manual labor and improving planting speed.
- Impact:
- Allows large areas to be planted quickly and accurately, saving time during critical planting windows.
- Reduces human errors associated with manual seeding methods.
- Example:
- Large-scale corn or soybean farms benefit from faster planting while maintaining high precision.
8. Reduction in Weed Competition
- How It Works:
- Precision planting ensures crops are evenly spaced, leaving less room for weeds to grow between plants.
- Impact:
- Reduces the need for herbicides and manual weeding.
- Promotes healthier crops by minimizing competition from unwanted plants.
- Example:
- In cereal crops like barley, precision planting reduces weed density, improving yield and quality.
9. Compatibility with Modern Technology
- How It Works:
- Many seed drills are integrated with GPS, sensors, and variable-rate technology to enhance precision.
- Smart seed drills adjust planting rates and depths based on soil variability or field zones.
- Impact:
- Optimizes planting for diverse field conditions, improving yield potential.
- Collects data for future decision-making and improved farm management.
- Example:
- Precision agriculture systems use GPS-enabled seed drills to create detailed planting maps for corn fields.
10. Reduced Soil Disturbance
- How It Works:
- Modern seed drills, especially no-till models, disturb only the narrow furrow where seeds are placed.
- Impact:
- Preserves soil structure and moisture while minimizing erosion.
- Enhances soil health and reduces energy costs associated with excessive tillage.
- Example:
- In no-till wheat farming, seed drills create minimal soil disturbance, conserving organic matter and moisture.
11. Improved Yield and Profitability
- How It Works:
- Precision planting ensures that all plants receive optimal growing conditions, leading to uniform and higher yields.
- Impact:
- Better crop performance translates to increased profitability for farmers.
- Example:
- Precision-seeded carrot fields produce uniformly sized vegetables, which command higher market prices.
12. Suitability for Diverse Crops
- How It Works:
- Seed drills can be adjusted for different seed types and sizes, making them versatile across various crops.
- Impact:
- Farmers can switch between crops like cereals, legumes, and vegetables without compromising planting accuracy.
- Example:
- A seed drill planting soybeans can be recalibrated to plant sunflower seeds with equal precision.
Conclusion
Seed drills significantly improve planting precision by ensuring uniform spacing, depth, and seeding rates, which are critical for maximizing germination, yield, and resource efficiency. By reducing labor requirements, minimizing waste, and adapting to various field conditions, seed drills are essential tools for modern agriculture, helping farmers achieve higher productivity and profitability while supporting sustainable farming practices.
Hashtags
#FarmTech #PrecisionPlanting #SeedTechnology #SustainableAgriculture #DigitalFarming #Agribusiness #FarmingSolutions #InnovativeFarming #SeedToHarvest #EfficientFarming #ModernAgriculture #SmartSeeding #PrecisionFarming #AgroTech #FarmingRevolution #SeedToYield #AdvancedFarming #AgriInnovation #SmartSeedingSolutions #FarmingTechnology