Technological advancements have significantly impacted food processing by improving efficiency, food safety, quality, and sustainability. Here’s how technology affects food processing:
1. Improved Efficiency and Productivity
- Impact: Automation and advanced machinery streamline production processes, reducing labor costs and increasing throughput. Technologies such as robotics, conveyor belts, and automated sorting systems enhance the speed and accuracy of food processing.
- Example: Automated packaging lines, robotic arms in sorting, and high-speed food processing machines.
2. Enhanced Food Safety
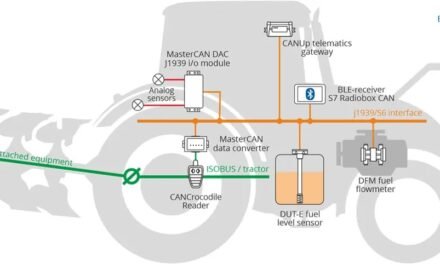
- Impact: New technologies help monitor and control food safety by detecting contaminants, bacteria, and pathogens. Advanced sensors, real-time data analytics, and traceability systems improve the safety and quality control of processed foods.
- Example: DNA-based testing for foodborne pathogens, real-time monitoring of temperature and humidity in storage, and blockchain for traceability.
3. Better Preservation Methods
- Impact: Innovations in preservation techniques, such as high-pressure processing (HPP), cold plasma, and UV light treatment, enable the preservation of food without compromising its nutritional value or taste.
- Example: HPP is used for juices, meats, and ready-to-eat meals, extending shelf life while retaining flavor and nutrients.
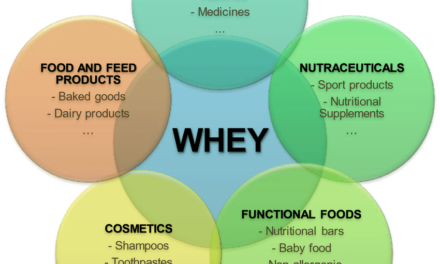
4. Customization and Product Innovation
- Impact: Technology allows for the creation of new food products and the customization of existing ones to meet changing consumer preferences. This includes personalized nutrition, plant-based alternatives, and functional foods with added health benefits.
- Example: Development of plant-based meat alternatives, functional beverages, and personalized nutrition apps.
5. Waste Reduction and Sustainability
- Impact: Advanced technologies help reduce food waste by improving supply chain logistics, optimizing production processes, and utilizing by-products for other purposes. This leads to more sustainable food production systems.
- Example: Upcycling food by-products into ingredients, using machine learning for supply chain optimization, and waste-to-energy technologies.
6. Improved Quality Control
- Impact: Innovations in food processing, such as precision cooking techniques and non-invasive inspection systems, help improve the consistency, texture, and taste of processed foods. Enhanced quality control ensures that products meet safety and nutritional standards.
- Example: Non-destructive testing using infrared and X-ray technology to inspect food for contaminants or defects.
7. Enhanced Nutritional Content
- Impact: Advances in food processing allow for better preservation of nutrients during processing, as well as the fortification of food with vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients to address dietary deficiencies.
- Example: Nutrient fortification in breakfast cereals, dairy products, and beverages to meet public health needs.
8. Automation and Data Analytics
- Impact: Automation and data analytics enable real-time tracking of production processes, allowing for better decision-making, resource allocation, and optimization of manufacturing practices.
- Example: Data-driven decision-making in inventory management, supply chain logistics, and energy use in processing plants.
Technological advancements in food processing help increase productivity, improve food quality and safety, enhance sustainability, and allow for the development of innovative products to meet consumer demand. These technologies play a key role in transforming the food industry to be more efficient, sustainable, and adaptable to changing market trends.