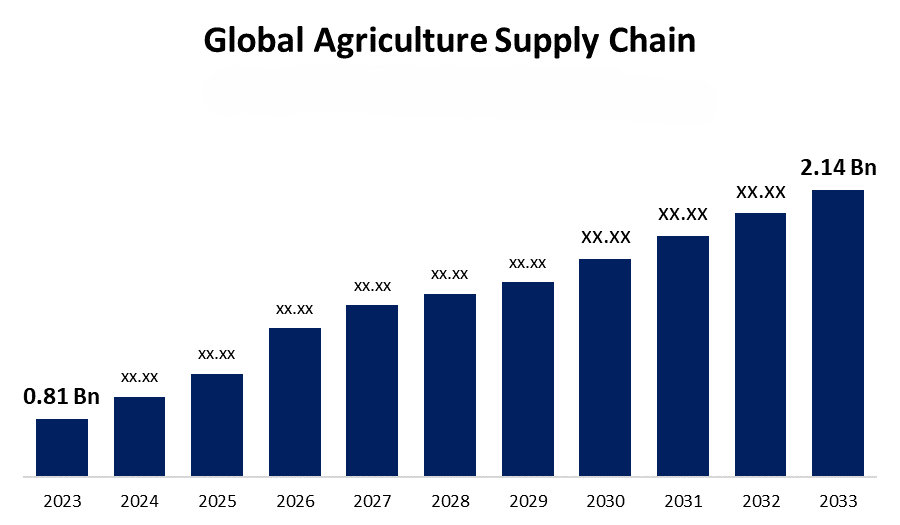
Grain milling plays a crucial role in the global agricultural supply chain by transforming raw agricultural commodities, such as wheat, corn, and rice, into a wide range of food products, animal feed, and industrial goods. Here’s how grain milling contributes to the global agricultural supply chain:
1. Processing Raw Materials into Consumable Products
- Transformation: Grain milling processes raw grains into a variety of products like flour, semolina, grits, and cereal. These processed products are essential ingredients in many food products, from bread to pasta to breakfast cereals.
- Impact: By converting grains into usable food products, milling serves as a vital intermediary step in ensuring that agricultural products are consumable and accessible to global markets.
2. Adding Value to Agricultural Commodities
- Value Addition: Milling adds value to raw agricultural commodities by processing grains into finished or semi-finished products. This increases the economic value of the grain and creates more product options for consumers.
- Impact: The value-added products from milling help increase the profitability of raw grain farmers and enhance the diversity of products available to consumers.
3. Facilitating Global Trade
- International Market Reach: Grain milling enables the export of processed products like flour, which are often traded internationally. These processed goods are easier to transport and store than raw grains, allowing for efficient global distribution.
- Impact: Milling supports the global trade of agricultural products by enabling easier transportation and trade of processed goods, which can reach markets in different countries.
4. Meeting Consumer Demand for Diverse Products
- Product Variety: Milling companies process a wide variety of grains (e.g., wheat, corn, rice, barley, oats) to create a range of products that cater to diverse consumer preferences, including gluten-free, whole grain, and organic options.
- Impact: By adapting to changing consumer preferences, the grain milling industry contributes to the availability of specialized food products and supports dietary needs worldwide.
5. Supplying Animal Feed
- Animal Feed Production: Milling also produces by-products such as bran, germ, and husks, which are used in animal feed. These by-products are an essential component of the agricultural supply chain for livestock production.
- Impact: Grain milling helps feed livestock, ensuring the availability of meat, dairy, and eggs for the global food system, thus supporting the entire agricultural supply chain from crop production to food on the table.
6. Contributing to Food Security
- Affordable Staple Foods: Milling plays a key role in ensuring the consistent and affordable supply of staple foods like bread, pasta, and rice, which are central to food security in many parts of the world.
- Impact: By producing large quantities of basic food products, milling helps stabilize food availability, especially in developing countries, where grains serve as a primary source of calories and nutrition.
7. Promoting Sustainable Agricultural Practices
- Sustainability Efforts: Modern grain milling practices are increasingly focused on sustainability, including minimizing waste, optimizing water use, and reducing energy consumption. Milling by-products are often used for alternative purposes, such as biofuel production or as ingredients in industrial products.
- Impact: Sustainable milling practices contribute to environmental conservation and help integrate the milling process into a circular economy, whereby by-products are repurposed rather than discarded.
8. Supporting the Livelihood of Farmers
- Market Access for Farmers: Grain mills provide a steady demand for raw grains, giving farmers access to markets and ensuring that their crops are processed into finished products that can be sold globally.
- Impact: Grain milling supports agricultural livelihoods by ensuring that grains are processed and marketed efficiently, benefiting farmers, millers, and consumers alike.
9. Creating Jobs and Economic Growth
- Employment Opportunities: The grain milling industry generates employment across the supply chain, from farm workers to mill operators to logistics staff.
- Impact: Grain milling is an important sector in many economies, providing jobs and contributing to local and national economic growth, particularly in regions where agriculture is a primary industry.
10. Enhancing Food Safety and Shelf Life
- Preserving Quality: Milling helps preserve the quality of grains by converting them into products that are easier to store and less perishable. Additionally, proper milling practices ensure that processed products are safe for consumption, free from contaminants or pathogens.
- Impact: By enhancing food safety and extending the shelf life of grains, milling contributes to reducing food waste and ensuring the availability of safe food products over extended periods.