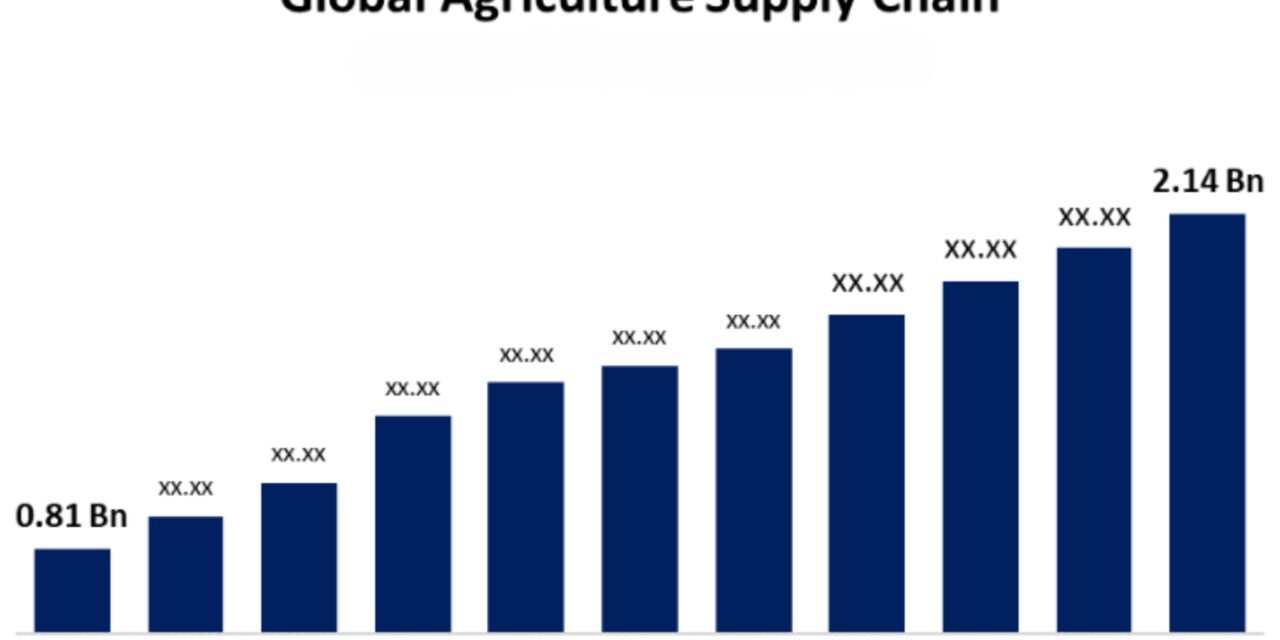
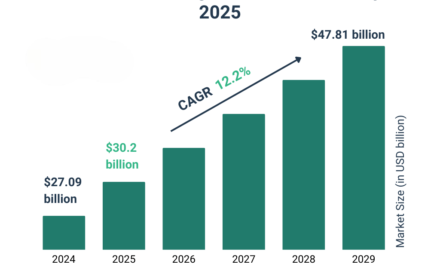
Oil extraction plays a vital role in the global agricultural supply chain in several ways:
1. Raw Material Sourcing
- Contribution: Oil extraction relies on various crops such as soybeans, sunflowers, rapeseed, palm oil, and olives, which are grown globally. These crops form the foundation of the agricultural supply chain, providing essential raw materials for oil production.
2. Value Addition
- Contribution: Oil extraction adds value to raw agricultural products by transforming seeds and fruits into oils that are used in food, cosmetics, biofuels, and industrial products. This value-added process enhances the profitability of agricultural goods and supports rural economies.
3. Economic Growth and Employment
- Contribution: The oil extraction industry provides significant employment opportunities in agriculture, manufacturing, and transportation. It supports local economies, especially in regions that rely on oilseed farming and processing, such as Southeast Asia (palm oil), South America (soybean oil), and Europe (rapeseed oil).
4. Trade and Global Markets
- Contribution: Oils like palm, soybean, and sunflower are major traded commodities in the global market. Oil extraction enables these agricultural products to be processed, packaged, and distributed internationally, contributing to global trade and economic integration. It also influences international pricing and supply chains.
5. Sustainability and Innovation
- Contribution: The oil extraction industry is increasingly focused on sustainable practices, such as certified sustainable palm oil (RSPO) or promoting organic farming methods. Innovations in oil extraction techniques, such as cold pressing and solvent-free processes, help address environmental concerns and improve the overall sustainability of the supply chain.
6. Food and Beverage Industry
- Contribution: Extracted oils are essential ingredients in the food and beverage industry, from cooking oils to salad dressings, margarine, and processed foods. The demand for different types of oils (e.g., plant-based, specialty oils) drives agricultural production, influencing crop choices and farming practices worldwide.
7. Biofuel Production
- Contribution: Oil extraction contributes significantly to biofuel production, particularly biodiesel made from soybean, canola, and palm oil. The growing demand for renewable energy sources has made biofuels a key component of the agricultural supply chain, impacting global energy markets.
8. Industrial and Non-Food Uses
- Contribution: Oils extracted from agricultural products are not only used in food but also the production of soaps, lubricants, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. This broadens the scope of the agricultural supply chain by linking the agricultural sector to various industries beyond food.
9. Waste Utilization
- Contribution: The by-products of oil extraction, such as oilseed cakes and meal, are used as animal feed or in the production of fertilizers. This circular approach minimizes waste and maximizes the utility of agricultural raw materials, promoting efficiency within the global supply chain.
10. Supply Chain Interdependence
- Contribution: Oil extraction connects farmers, manufacturers, distributors, and consumers in a complex, interdependent global supply chain. Efficient oil extraction methods help maintain a steady supply, meet market demands, and support food security by ensuring the availability of essential ingredients across markets.