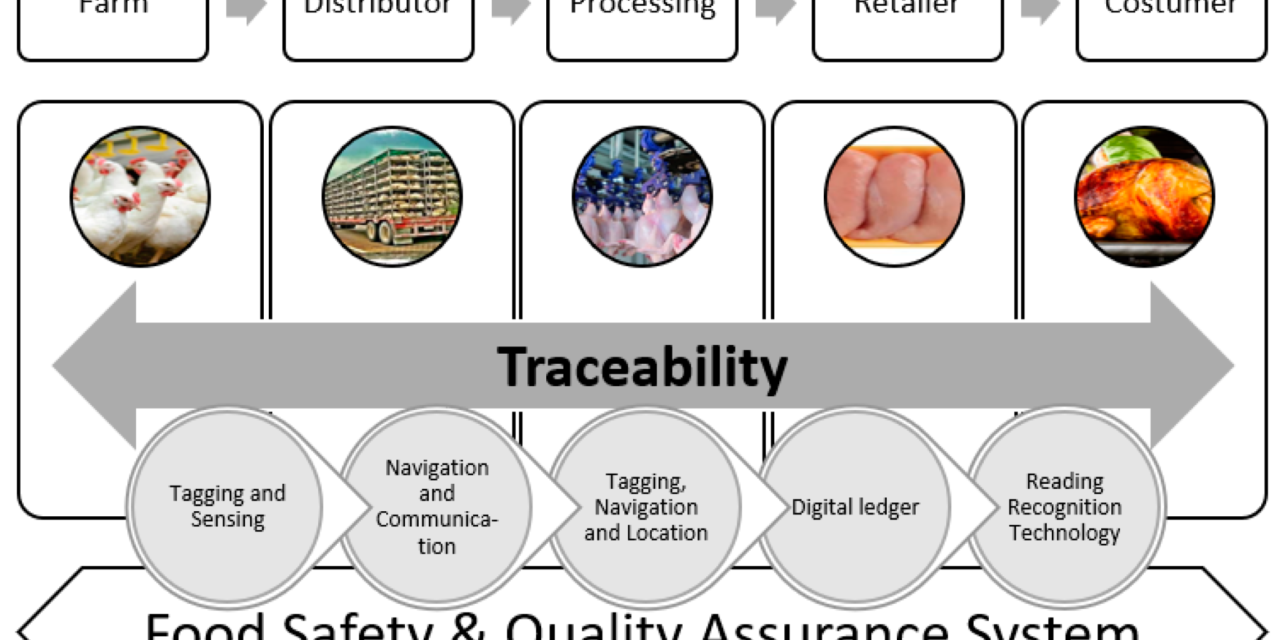
Blockchain technology enhances traceability in food manufacturing by creating a secure, transparent, and immutable digital record of every stage in the food supply chain. This technology improves food safety, quality assurance, and consumer trust. Here’s how blockchain achieves this:
1. Immutable Record of Transactions
- How it Works: Blockchain stores data in a decentralized ledger where each transaction is recorded in a tamper-proof block linked to the previous one.
- Impact on Traceability: Every stage in the food production process—harvesting, processing, packaging, and distribution—is recorded and time-stamped. This ensures that the data is reliable and cannot be altered.
2. End-to-End Supply Chain Visibility
- How it Works: Blockchain provides a unified platform for all stakeholders, including farmers, processors, distributors, and retailers, to input and access data.
- Impact on Traceability: Stakeholders can track a product’s journey from farm to fork, identifying its origin, handling conditions, and current status. For example, a consumer can scan a QR code on a product to view its entire history.
3. Enhanced Food Safety
- How it Works: Blockchain allows rapid identification of contamination sources in case of foodborne illness outbreaks.
- Impact on Traceability: By pinpointing the affected batches and their origins, manufacturers can initiate targeted recalls, reducing waste and mitigating risks to public health.
4. Verification of Authenticity and Certifications
- How it Works: Certifications such as organic, fair trade, or non-GMO can be stored on the blockchain and verified by trusted authorities.
- Impact on Traceability: Ensures products meet the standards and prevent fraudulent labeling. Consumers can verify the authenticity of claims directly.
5. Integration with IoT Devices
- How it Works: IoT devices, such as temperature and humidity sensors, collect real-time data during storage and transport, which is uploaded to the blockchain.
- Impact on Traceability: Ensures that products have been stored under optimal conditions, maintaining quality and compliance with safety standards.
6. Transparency for Consumers
- How it Works: Blockchain platforms allow consumers to access detailed product information, such as sourcing, production practices, and sustainability metrics.
- Impact on Traceability: Builds consumer trust by offering visibility into the supply chain and addressing concerns about food origin and ethical practices.
7. Reducing Fraud and Counterfeiting
- How it Works: Blockchain records prevent unauthorized alterations, making it difficult for counterfeit or substandard products to enter the supply chain.
- Impact on Traceability: Enhances brand protection and ensures consumers receive genuine products.
8. Facilitating Regulatory Compliance
- How it Works: Blockchain automates record-keeping and provides instant access to traceability data required for audits and compliance checks.
- Impact on Traceability: Reduces manual paperwork, improves accuracy, and simplifies compliance with food safety regulations like FSMA or EU traceability laws.
9. Streamlined Recall Processes
- How it Works: Blockchain enables rapid identification of specific product batches and their distribution routes.
- Impact on Traceability: Minimizes the scope and time required for recalls, reducing economic losses and protecting consumer health.
10. Collaboration Across Stakeholders
- How it Works: Blockchain fosters a shared ecosystem where stakeholders collaborate to ensure data accuracy and integrity.
- Impact on Traceability: Encourages accountability and enhances trust across the supply chain.
Examples of Blockchain in Food Manufacturing
- IBM Food Trust: Used by companies like Walmart, Nestlé, and Unilever to enhance food traceability.
- Provenance: Tracks seafood from fishing vessels to restaurants, ensuring ethical sourcing.
- Everledger: Monitors the origin and authenticity of premium products like wine and cocoa.
Benefits of Blockchain in Food Traceability
- Improved Transparency: Real-time access to traceability data for all stakeholders.
- Increased Efficiency: Faster identification of bottlenecks or issues in the supply chain.
- Enhanced Consumer Trust: Offers verifiable proof of ethical and sustainable practices.
- Reduced Risk: Mitigates food fraud, contamination, and regulatory non-compliance risks.
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing food manufacturing by creating a trustworthy and efficient traceability system, ensuring that food products meet safety, quality, and ethical standards.
Hashtags
#FoodSecurity #TraceableSupplyChain #BlockchainRevolution #FoodIndustryInnovation #DigitalTransformation #FoodSafetyFirst #EfficientSupplyChain #BlockchainBenefits #FoodQualityControl #InnovativeTechnology #SustainableFoodSystem #TransparentFoodIndustry #FoodTraceabilityMatters #SmartFoodSolutions #BlockchainIntegration #FoodSafetyStandards #TechForGood #SupplyChainEfficiency #FoodProductionTech #TraceableIngredients