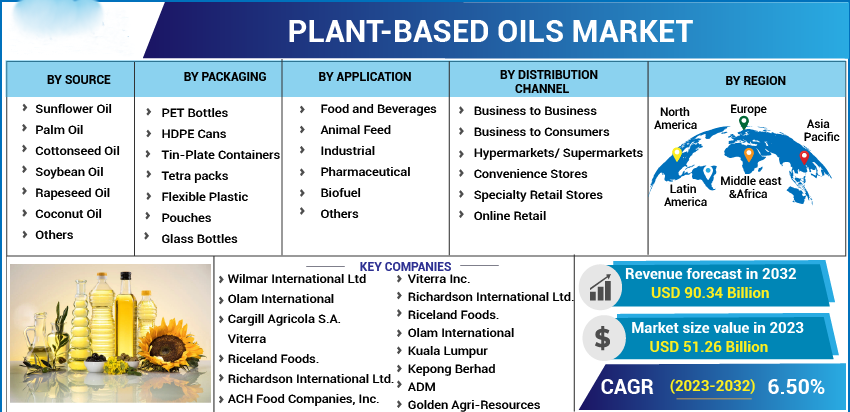
The increasing demand for plant-based oils is reshaping the oil industry in multiple ways, influencing everything from production and product development to sustainability practices and market dynamics. Here’s a detailed look at the key changes:
1. Shift in Consumer Preferences
Health and Wellness Trends
- Consumers are favoring plant-based oils for their perceived health benefits, such as being lower in saturated fats and containing heart-healthy fatty acids (e.g., omega-3 and omega-6).
- Oils like olive, avocado, coconut, and flaxseed are gaining popularity for their functional properties and nutrient profiles.
Vegan and Plant-Based Diets
- The rise of veganism and plant-based diets has driven demand for oils derived from plants, both for cooking and as ingredients in processed plant-based foods.
- Coconut oil, for instance, is widely used in vegan alternatives for butter, cheese, and desserts.
2. Expansion of Specialty Oils
- High-Oleic Oils: Oils like high-oleic sunflower and canola are gaining traction due to their stability, longer shelf life, and health benefits.
- Functional and Nutritional Oils: Specialty oils such as flaxseed, hemp seed, and chia seed oil are marketed for their omega-3 content and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Exotic Oils: Oils like argan, moringa, and sesame are emerging in niche markets, particularly in cosmetics, health supplements, and gourmet cooking.
3. Growth of Clean-Label and Organic Products
- Consumers demand transparency, leading to increased production of organic, cold-pressed, and minimally processed oils.
- Certifications like USDA Organic, Non-GMO Project Verified, and Fair Trade are becoming essential for market competitiveness.
4. Increased Focus on Sustainability
Sustainable Sourcing
- The environmental impact of oil production, particularly palm oil, has led to greater scrutiny. Certification initiatives such as RSPO (Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil) and RTRS (Round Table on Responsible Soy) are promoting sustainable practices.
- Alternatives to palm oil, like coconut, sunflower, and canola, are gaining prominence due to sustainability concerns.
Circular Economy Practices
- Companies are repurposing by-products, such as oilseed meal for animal feed or bioenergy, to reduce waste and improve profitability.
- Biodiesel production from plant-based oils and waste oils contributes to the global shift toward renewable energy.
5. Innovation in Processing Technologies
Cold Pressing and Minimal Processing
- Advanced cold-pressing techniques preserve the natural flavors, nutrients, and functional properties of oils, catering to health-conscious consumers.
- Minimal processing is becoming a key selling point for premium oils.
Enzymatic and Fermentation-Based Extraction
- Novel extraction methods, such as enzymatic processes or fermentation, are gaining traction to produce high-quality oils while reducing environmental impact.
6. Diversification in Applications
Food and Beverage Industry
- Plant-based oils are increasingly used as ingredients in vegan and plant-based products, including meat and dairy substitutes.
- High-stability oils like canola and high-oleic sunflower oil are widely used in snack foods, baked goods, and frying applications.
Personal Care and Cosmetics
- Plant-based oils like argan, coconut, and almond oil are heavily used in skincare, haircare, and other cosmetic products.
- The “natural beauty” trend is driving demand for oils free from synthetic additives.
Industrial Uses
- Oils such as castor and soybean oil are being utilized in bio-lubricants, biodegradable plastics, and other industrial applications.
7. Market Globalization and Regional Shifts
Emerging Markets
- Rising incomes and urbanization in Asia, Africa, and Latin America are driving demand for plant-based oils for cooking and processed foods.
- India and China are major growth markets for sunflower, soybean, and palm oils.
Export Growth
- Countries like Indonesia and Malaysia continue to dominate palm oil exports, while the U.S., Brazil, and Argentina lead in soybean oil production.
- Mediterranean countries maintain strong positions in olive oil exports.
8. Competition with Animal-Based Fats
- The shift away from animal fats (e.g., butter, lard) has boosted demand for plant-based oils in both home cooking and food manufacturing.
- Food manufacturers are replacing animal fats with plant-based oils to create vegan-friendly products and meet clean-label demands.
9. Technological Advancements in Farming
- High-Yield Varieties: Development of drought-resistant and pest-resistant oilseed crops, such as soybeans, canola, and sunflower, to meet rising demand.
- Precision Agriculture: Use of technologies like drones, IoT sensors, and satellite imagery to optimize oilseed cultivation and reduce waste.
10. Regulatory Changes and Industry Standards
- Governments are promoting plant-based oils by setting limits on trans fats, incentivizing the use of healthy oils, and encouraging sustainable practices.
- Regulatory frameworks for labeling, organic certification, and sustainability are becoming more stringent, driving industry-wide standardization.
11. Challenges in Meeting Demand
- Environmental Concerns: Large-scale production of some plant-based oils, like palm oil, is associated with deforestation, biodiversity loss, and carbon emissions.
- Supply Chain Constraints: Limited availability of certain specialty oils and fluctuations in raw material costs impact pricing and accessibility.
- Market Competition: Competition among plant-based oil types (e.g., olive oil vs. avocado oil) requires producers to differentiate through branding and innovation.
Conclusion
The rising demand for plant-based oils is driving innovation, sustainability, and diversification across the industry. Producers are adapting to meet health-conscious consumer preferences, environmental concerns, and evolving market needs. This transformation is reshaping the global edible oil market, creating new opportunities while also presenting challenges related to scalability, sustainability, and market competition.
Hashtags
#EcoConsciousEating #CleanEating #SustainableLiving #PlantBasedDiet #HealthyFats #OrganicOils #EcoFriendlyLiving #GreenEating #SustainableFarming #HealthyPlanet #NaturalOils #EcoFriendlyProducts #SustainableSolutions #HealthyChoices #EcoFriendlyAlternatives #GreenRevolution #SustainableFoods #HealthyLifestyle #EcoFriendlyConsumption #GreenEconomy