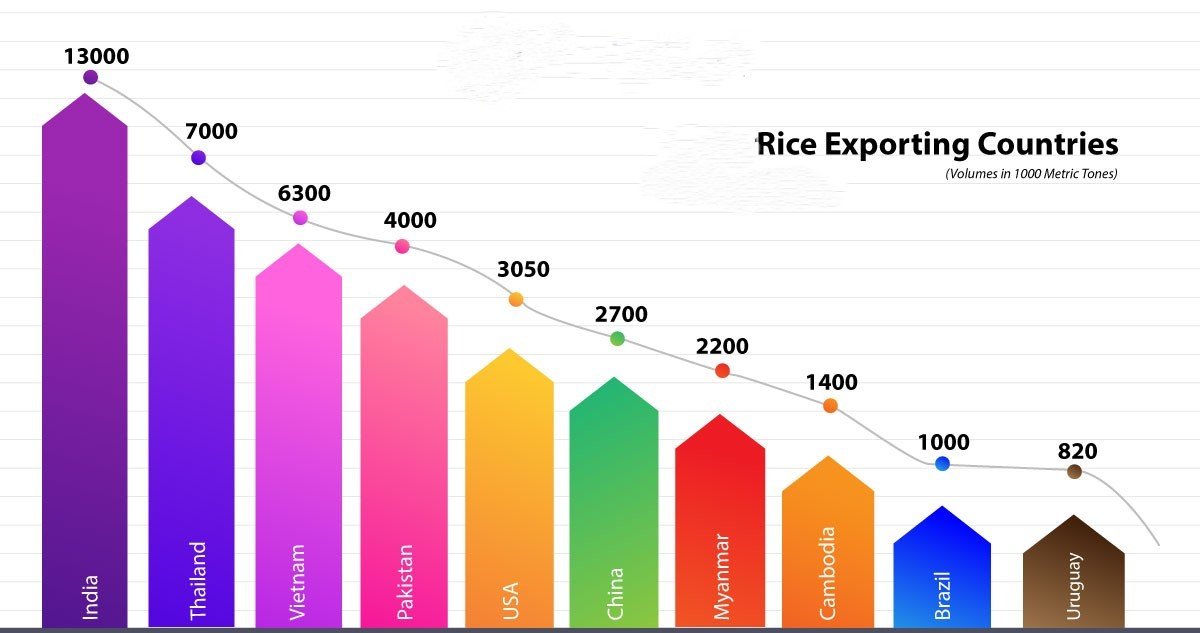
Rice producers in developing countries have significant export opportunities due to the increasing global demand for rice, driven by population growth, changing dietary preferences, and expanding trade networks. However, capitalizing on these opportunities requires strategic planning, quality improvements, and an understanding of global market trends. Here’s an overview of the key export opportunities for rice producers in developing countries:
1. Growing Demand for Specialty Rice
- Opportunity:
- Niche markets for specialty rice varieties like Basmati, Jasmine, organic, and aromatic rice are growing in developed countries.
- Target Markets:
- In high-income countries such as the U.S., Europe, and Japan, consumers pay premiums for quality and origin-specific rice.
- Action Steps:
- Focus on producing high-quality specialty rice with unique characteristics.
- Obtain certifications like Geographical Indications (GI) and organic certifications to increase market value.
2. Increasing Demand in Africa
- Opportunity:
- Africa imports a significant portion of its rice, driven by rapid urbanization and changing consumption patterns.
- Key Markets:
- Nigeria, Senegal, Côte d’Ivoire, and Ghana.
- Action Steps:
- Target lower-priced, non-aromatic rice varieties.
- Develop efficient supply chains to meet consistent demand.
3. Expanding Middle Eastern Market
- Opportunity:
- The Middle East has a strong demand for premium rice, including Basmati and aromatic varieties.
- Key Markets:
- Saudi Arabia, UAE, Iran, and Iraq.
- Action Steps:
- Build relationships with importers in the Middle East.
- Meet Halal certification requirements to cater to Muslim consumers.
4. Organic and Sustainable Rice Markets
- Opportunity:
- Organic rice is gaining traction in health-conscious markets such as Europe, North America, and Australia.
- Key Markets:
- Germany, France, U.S., and Canada.
- Action Steps:
- Transition to organic farming practices and obtain organic certifications.
- Highlight sustainable farming methods to appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
5. Processed Rice Products
- Opportunity:
- Value-added products like parboiled rice, rice flour, rice noodles, and rice snacks are in demand globally.
- Key Markets:
- High-income countries and emerging economies with a growing convenience food sector.
- Action Steps:
- Invest in rice processing facilities to produce value-added products.
- Collaborate with food manufacturers for B2B exports.
6. Demand from Food Security Programs
- Opportunity:
- Governments and international organizations procure rice for food security programs, especially in low-income and food-deficit regions.
- Key Markets:
- Countries in Sub-Saharan Africa, and South Asia, and humanitarian aid programs by organizations like the World Food Programme (WFP).
- Action Steps:
- Comply with international quality and safety standards.
- Participate in tenders for public procurement and aid programs.
7. Expanding Regional Trade
- Opportunity:
- Regional trade agreements and partnerships within economic blocs such as ASEAN, SAARC, and ECOWAS create export opportunities.
- Key Markets:
- Neighboring countries with high rice demand.
- Action Steps:
- Leverage reduced tariffs and streamlined trade regulations under regional trade agreements.
- Build efficient cross-border supply chains.
8. Diversifying Product Offerings
- Opportunity:
- Export demand is not limited to polished white rice; broken rice and rice bran are also in demand for animal feed and industrial applications.
- Key Markets:
- Animal feed producers in Asia and bioethanol industries in Europe.
- Action Steps:
- Explore export markets for by-products like broken rice, rice bran oil, and husk for renewable energy.
9. Exporting to Rice-Deficit Countries
- Opportunity:
- Countries with limited rice production and high consumption rely heavily on imports.
- Key Markets:
- West Africa, the Caribbean, and the Middle East.
- Action Steps:
- Focus on producing low-cost, high-yield varieties to meet bulk requirements.
- Build long-term contracts with importers in rice-deficit countries.
10. Meeting Quality and Safety Standards
- Opportunity:
- Developing countries can access premium markets by complying with international quality and food safety standards.
- Key Standards:
- HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points).
- ISO certifications for quality and environmental management.
- Phytosanitary certifications for pest-free products.
- Action Steps:
- Invest in quality control systems and laboratory testing.
- Use advanced packaging and storage methods to maintain quality during transportation.
11. Leveraging E-Commerce Platforms
- Opportunity:
- Global e-commerce platforms offer direct access to consumers and businesses.
- Platforms:
- Alibaba, Amazon, and region-specific platforms like Flipkart (India) and Shopee (Southeast Asia).
- Action Steps:
- Market rice products on e-commerce platforms, emphasizing unique qualities like organic, sustainable, or traditional.
- Use digital marketing to reach international buyers.
12. Climate-Resilient Rice
- Opportunity:
- Climate change is driving demand for drought-resistant and salt-tolerant rice varieties.
- Key Markets:
- Regions prone to climate stress, such as Africa and South Asia.
- Action Steps:
- Invest in research and development of climate-resilient rice varieties.
- Promote these varieties to governments and NGOs working in climate-vulnerable regions.
13. Government Support and Export Incentives
- Opportunity:
- Many governments provide subsidies, incentives, and support for rice exporters.
- Examples:
- Export promotion schemes, tax exemptions, and reduced-interest loans.
- Action Steps:
- Work with national trade bodies and export promotion agencies to access incentives.
- Participate in international trade fairs and buyer-seller meets.
Challenges to Address
- Quality Control:
- Ensure consistent quality to meet international buyer expectations.
- Logistics:
- Address challenges in shipping, storage, and handling to maintain product quality.
- Market Competition:
- Compete with major rice exporters like Thailand, Vietnam, and India.
- Trade Barriers:
- Navigate tariffs, non-tariff barriers, and phytosanitary regulations.
Conclusion
Rice producers in developing countries have diverse export opportunities, ranging from specialty rice and processed products to bulk exports for food security programs. By focusing on quality, sustainability, and value addition while leveraging trade agreements and government support, producers can enhance their competitiveness in global markets. Strategic marketing and compliance with international standards will be key to long-term success.
Hashtags
#RiceProduction #InternationalTrade #AgriculturalExports #RiceSupplyChain #RiceDemand #RiceEconomy #RiceHarvest #ExportingRice #RiceBusiness #RiceMarket #RiceExporters #RiceImporters #RiceQuality #RiceVarieties #RiceConsumption #RicePrices #RiceDistribution #RiceSustainability #RiceTradeAgreements #RiceIndustryUpdates