Small-scale farming can be highly profitable with the right choice of vegetables, especially those that have high market demand, fast growth cycles, and the potential for value addition. Here’s a list of the most profitable vegetables to grow in small-scale farming, along with key considerations:
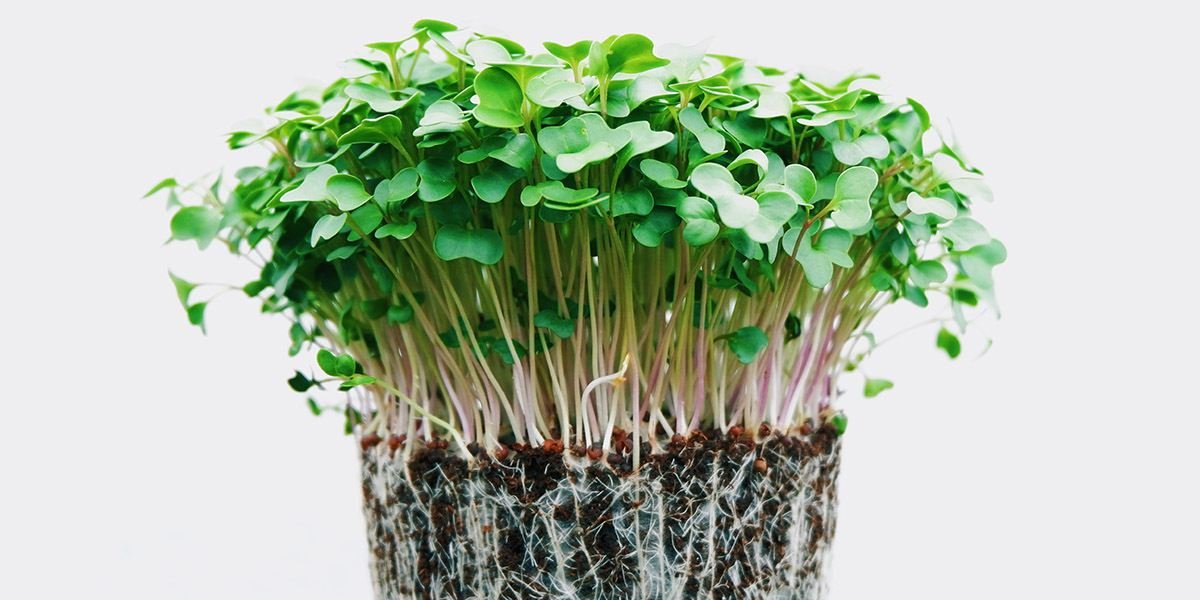
1. Microgreens
- Why Profitable:
- High market value ($20–50 per pound).
- Fast growth cycle (7–21 days).
- Requires minimal space and inputs.
- Popular Varieties:
- Arugula, kale, radish, broccoli, and basil.
- Market Opportunities:
- Health-conscious consumers, restaurants, and local farmers’ markets.
- Tips for Success:
- Use vertical farming or hydroponics to maximize yield.
- Ensure proper lighting and temperature control.
2. Lettuce
- Why Profitable:
- High demand year-round for fresh and salad greens.
- Quick growth (30–60 days depending on variety).
- Popular Varieties:
- Romaine, butterhead, and loose-leaf lettuces.
- Market Opportunities:
- Direct sales to restaurants, grocery stores, or CSA (Community Supported Agriculture) programs.
- Tips for Success:
- Use staggered planting for continuous harvests.
- Consider hydroponic or greenhouse systems for better yields and quality.
3. Herbs
- Why Profitable:
- High price per unit weight.
- Low input costs and can be grown in small spaces.
- Popular Varieties:
- Basil, cilantro, parsley, mint, rosemary, and thyme.
- Market Opportunities:
- Culinary markets, herbal tea producers, and cosmetic or essential oil industries.
- Tips for Success:
- Grow perennial herbs for recurring harvests.
- Focus on organic production for premium pricing.
4. Spinach
- Why Profitable:
- Fast growth (4–6 weeks to harvest).
- High nutritional value drives consistent demand.
- Market Opportunities:
- Fresh produce markets, pre-packed salads, and smoothie ingredient suppliers.
- Tips for Success:
- Use high-yield varieties and practice crop rotation to maintain soil fertility.
- Target winter and early spring markets for premium prices.
5. Tomatoes
- Why Profitable:
- Versatile crop with high demand for fresh and processed products.
- Potential for high yields in greenhouse or hydroponic systems.
- Popular Varieties:
- Cherry, heirloom, beefsteak, and Roma tomatoes.
- Market Opportunities:
- Fresh market sales, sauces, salsas, and canned products.
- Tips for Success:
- Focus on disease-resistant varieties.
- Use trellising systems for better airflow and higher productivity.
6. Peppers
- Why Profitable:
- High market value for specialty peppers (e.g., chili, bell, and sweet varieties).
- Popular Varieties:
- Jalapeño, habanero, bell peppers, and shishito.
- Market Opportunities:
- Fresh produce markets, spice production, and value-added products like hot sauces.
- Tips for Success:
- Grow colorful bell peppers for higher prices.
- Extend the growing season using greenhouses or tunnels.
7. Garlic
- Why Profitable:
- High demand and excellent storage life.
- Minimal maintenance once planted.
- Popular Varieties:
- Softneck garlic for storage; hardneck garlic for gourmet markets.
- Market Opportunities:
- Fresh bulbs, garlic powder, and black garlic for gourmet markets.
- Tips for Success:
- Target specialty markets for organic and gourmet garlic.
- Plant in the fall for a summer harvest.
8. Onions and Shallots
- Why Profitable:
- Staple ingredients with consistent demand.
- High-value potential for shallots and specialty onions.
- Popular Varieties:
- Red, white, and yellow onions; French shallots.
- Market Opportunities:
- Fresh produce sales and value-added products like caramelized onions.
- Tips for Success:
- Use drip irrigation to improve water efficiency.
- Choose varieties suited for long-term storage.
9. Zucchini and Summer Squash
- Why Profitable:
- High yields per plant and short growth cycle (40–60 days).
- Demand in fresh and processed markets.
- Market Opportunities:
- Fresh market sales, frozen vegetables, and vegetable noodles.
- Tips for Success:
- Harvest young for better flavor and higher market value.
- Use disease-resistant varieties to minimize losses.
10. Broccoli
- Why Profitable:
- High-value vegetables with increasing demand for fresh and frozen options.
- Market Opportunities:
- Fresh produce markets, frozen food suppliers, and pre-packed salad mixes.
- Tips for Success:
- Focus on early or late-season production to avoid heat stress.
- Grow in well-drained soil with consistent irrigation.
11. Mushrooms
- Why Profitable:
- High-value crop with low space requirements.
- It can be grown indoors year-round.
- Popular Varieties:
- Oyster, shiitake, and button mushrooms.
- Market Opportunities:
- Gourmet restaurants, health food stores, and specialty markets.
- Tips for Success:
- Use controlled environments for better yields.
- Offer value-added products like dried or powdered mushrooms.
12. Cucumbers
- Why Profitable:
- Fast-growing crop with high demand for fresh and pickling varieties.
- Market Opportunities:
- Fresh markets, pickling industries, and specialty salad producers.
- Tips for Success:
- Use trellises for higher yields and better-quality fruit.
- Focus on thin-skinned varieties for premium pricing.
13. Asparagus
- Why Profitable:
- High market value for a perennial crop with long-term yield potential.
- Market Opportunities:
- Fresh produce markets and gourmet retailers.
- Tips for Success:
- Requires initial investment but provides yields for up to 20 years.
- Target early spring markets for premium prices.
14. Kale
- Why Profitable:
- Consistently high demand due to health trends.
- Hardy crop that grows well in diverse climates.
- Market Opportunities:
- Fresh salads, smoothie ingredients, and dehydrated kale chips.
- Tips for Success:
- Grow organic to target health-conscious consumers.
- Extend the growing season with row covers.
15. Carrots
- Why Profitable:
- High demand for fresh and processed carrots.
- Long shelf life and ease of storage.
- Market Opportunities:
- Fresh produce, juicing, and baby carrot markets.
- Tips for Success:
- Grow colorful varieties for specialty markets.
- Use raised beds for uniform roots and higher yields.
General Tips for Small-Scale Farming Profitability
- Choose High-Value Crops:
- Focus on vegetables that offer higher returns per square foot.
- Emphasize Quality:
- Organic, pesticide-free, or heirloom varieties often command premium prices.
- Value Addition:
- Process vegetables into products like sauces, powders, or dried snacks to increase profitability.
- Season Extension:
- Use greenhouses, high tunnels, or row covers to produce off-season vegetables.
- Market Directly:
- To maximize margins, sell directly to consumers through farmers’ markets, CSAs, or online platforms.
- Diversify:
- Grow a mix of crops to spread risk and cater to varied market demands.
By carefully selecting the right crops, adopting efficient farming techniques, and leveraging local and niche markets, small-scale farmers can achieve high profitability while maintaining sustainability.
Hashtags
farmfresh #healthyharvest #communitysupportedagriculture #farmersmarket #farmlife #greenthumb #growyourownfood #farmersoffacebook #farmersunited #farmersfeedtheworld #farmersforchange #farmersforthefuture #farmersforsustainability #farmersforsuccess #farmersforgood #farmersforprofit #farmersfortheplanet #farmersforhealth #farmersforlife #farmersforthepeople