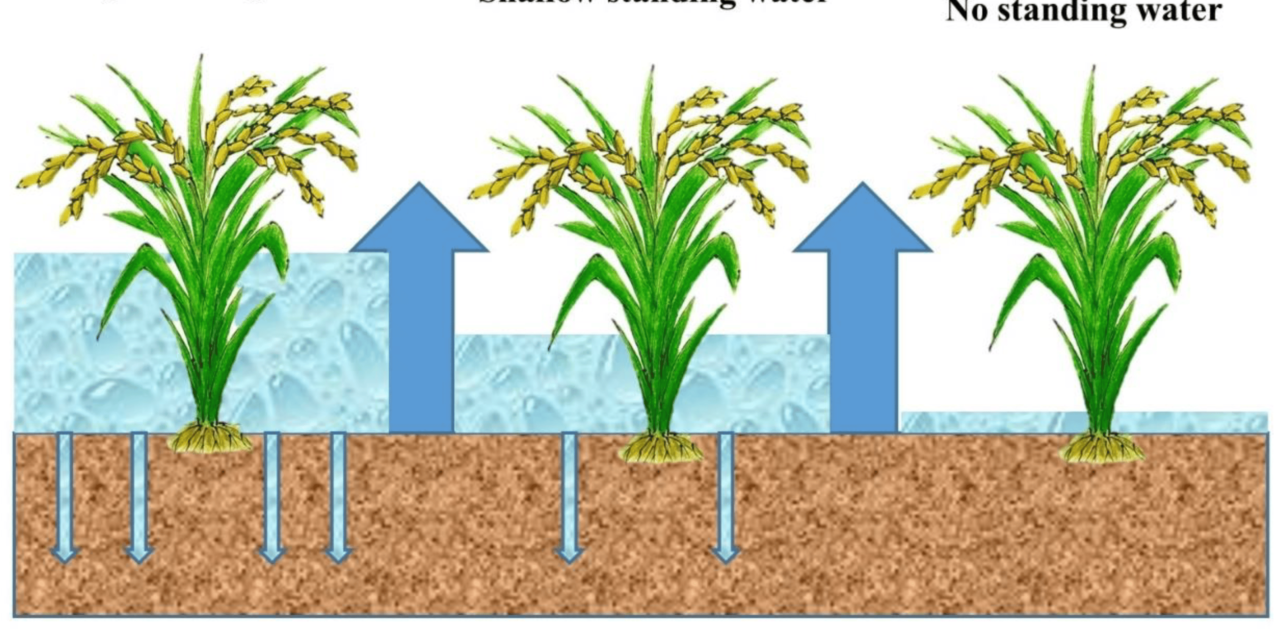
Water management plays a critical role in increasing rice yield by optimizing resource use, improving crop health, and mitigating risks like drought and waterlogging. Rice is highly water-intensive, with traditional flooded paddy systems requiring substantial water inputs. Effective water management ensures that water is used efficiently and sustainably while enhancing productivity. Here’s how water management impacts rice yields:
1. Providing Adequate Moisture for Growth Stages
- Importance: Rice requires consistent moisture at specific growth stages for optimal development.
- Critical Stages:
- Germination and seedling establishment.
- Tillering (formation of shoots).
- Panicle initiation and grain filling.
- Critical Stages:
- Impact on Yield:
- Sufficient water during these stages promotes healthy root development, tillering, and grain formation.
- Practice: Scheduled irrigation ensures water availability during critical growth periods.
2. Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD)
- What It Is: A water-saving technique that allows fields to dry out intermittently before re-irrigation.
- Benefits:
- Improves oxygen availability to roots, enhancing nutrient uptake and root health.
- Reduces methane emissions while maintaining or increasing yields.
- Impact on Yield:
- Boosts productivity by reducing water stress and nutrient deficiencies.
- Example: AWD has shown up to a 20% increase in yields compared to continuous flooding in certain regions.
3. Maintaining Proper Flooding Levels
- What It Is: Keeping a thin water layer (2-5 cm) rather than deep flooding.
- Benefits:
- Reduces weed growth, minimizing competition for nutrients.
- Prevents waterlogging and root suffocation.
- Impact on Yield:
- Promotes balanced nutrient uptake, improving plant health and grain quality.
- Practice: Use laser leveling to ensure uniform water distribution and proper depth.
4. Improved Drainage Systems
- What It Is: Systems to remove excess water during periods of heavy rainfall or over-irrigation.
- Benefits:
- Prevents waterlogging, which can stunt growth and increase disease risk.
- Enhances aeration, supporting microbial activity and nutrient cycling.
- Impact on Yield:
- Reduces crop losses from waterborne diseases and anaerobic stress.
- Practice: Install field drains or ditches for controlled water removal.
5. Efficient Irrigation Systems
- What It Is: Techniques like furrow irrigation, sprinkler systems, or drip irrigation for water application.
- Benefits:
- Reduces water waste through targeted delivery.
- Prevents runoff and deep percolation losses.
- Impact on Yield:
- Ensures consistent moisture, even during dry spells, leading to healthier plants and higher grain counts.
- Example: Drip irrigation in upland rice cultivation can improve water-use efficiency and yields.
6. Laser Land Leveling
- What It Is: A technology that ensures fields are perfectly leveled.
- Benefits:
- Prevents water pooling in low spots and ensures uniform water coverage.
- Improves water-use efficiency by up to 50%.
- Impact on Yield:
- Ensures even crop growth and higher yields across the field.
- Example: Farmers in India and Pakistan using laser leveling report increased yields and reduced water usage.
7. Rainwater Harvesting and Storage
- What It Is: Capturing and storing rainwater for irrigation during dry periods.
- Benefits:
- Provides a consistent water supply, reducing dependence on unreliable rainfall.
- Supports supplementary irrigation during critical growth stages.
- Impact on Yield:
- Minimizes water stress, preventing stunted growth and low grain fill.
- Example: Small ponds and reservoirs in Southeast Asia have improved yields by providing water during droughts.
8. Water Quality Management
- What It Is: Ensuring the water used for irrigation is free from harmful salts, chemicals, and pathogens.
- Benefits:
- Prevents soil salinization and nutrient imbalances.
- Reduces the risk of diseases caused by contaminated water.
- Impact on Yield:
- Improves plant health and grain quality, leading to higher market value.
- Practice: Use filtration systems or manage water sources to ensure quality.
9. Soil Moisture Monitoring
- What It Is: Using sensors or manual tools to measure soil moisture levels and guide irrigation decisions.
- Benefits:
- Prevents over-irrigation and water stress.
- Reduces water use without compromising crop growth.
- Impact on Yield:
- It supports precise irrigation timing and optimizes plant hydration and nutrient absorption.
- Example: Soil moisture sensors integrated with IoT systems help farmers maintain optimal moisture levels.
10. Integration with Fertilizer Application
- What It Is: Combining irrigation with nutrient delivery (fertigation).
- Benefits:
- Ensures efficient nutrient uptake by synchronizing water and fertilizer availability.
- Reduces nutrient losses due to runoff or leaching.
- Impact on Yield:
- Enhances plant growth and increases the number of productive tillers and grains per panicle.
- Example: Nitrogen and potassium applied through irrigation systems improve yields significantly in hybrid rice.
11. Drought-Resistant Varieties
- What It Is: Cultivating rice varieties bred for higher tolerance to water scarcity.
- Benefits:
- Requires less water while maintaining productivity.
- Provides resilience during unpredictable rainfall or irrigation supply.
- Impact on Yield:
- Ensures consistent production even in water-limited conditions.
- Example: Varieties like “Sahbhagi Dhan” in India have shown 30% higher yields under drought stress.
12. Climate-Smart Water Management
- What It Is: Adjusting water management strategies based on climate patterns and forecasts.
- Benefits:
- Mitigates risks from climate variability, such as droughts or floods.
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions (methane and nitrous oxide) from waterlogged fields.
- Impact on Yield:
- Enhances productivity by aligning water use with environmental conditions.
- Example: Farmers using weather forecasts for irrigation scheduling achieve better yields and water efficiency.
13. Community-Based Water Management
- What It Is: Collaborative management of shared water resources among farmers.
- Benefits:
- Ensures equitable water distribution.
- Reduces overuse and disputes over shared water sources.
- Impact on Yield:
- Promotes optimal water availability for all farmers, improving overall productivity.
- Example: Water user associations in Southeast Asia help smallholder farmers maintain consistent yields.
14. Training and Capacity Building
- What It Is: Educating farmers on water-saving techniques and technologies.
- Benefits:
- Increases awareness and adoption of efficient water practices.
- Encourages sustainable water use at the community level.
- Impact on Yield:
- Facilitates the transition to modern methods, boosting yields and profitability.
- Example: Training programs on AWD have resulted in significant yield improvements in countries like Bangladesh and the Philippines.
Conclusion
Effective water management is central to increasing rice yields, as it ensures that crops receive optimal hydration at critical stages of growth while minimizing resource wastage. Techniques like AWD, laser land leveling, and soil moisture monitoring allow farmers to optimize water use, improve plant health, and reduce environmental impact. By adopting these practices and leveraging advanced technologies, farmers can achieve sustainable productivity, even in the face of water scarcity and climate change.
Hashtags
#WaterConservation #PrecisionFarming #SustainableDevelopment #IrrigationTechnology #RiceHarvest #EnvironmentalSustainability #WaterSavings #OrganicFarming #ClimateChange #RiceFields #WaterScarcity #AgTech #SustainableFood #WaterUseEfficiency #RiceVarieties #GreenFarming #WaterSecurity #SustainableLiving #RiceIndustry #WaterFootprint